Financial Accounting Online Tutor, Practice Problems & Exam Prep


Liabilities are amounts owed to others relating to loans, extensions of credit, and other obligations arising in the course of business. Implicit to the notion of a liability best accounting software for advertising agencies is the idea of an “existing” obligation to pay or perform some duty. The 500 year-old accounting system where every transaction is recorded into at least two accounts.
Assets
- ” The answer to this question depends on the legal form of the entity; examples of entity types include sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations.
- Our PRO users get lifetime access to our accounting equation visual tutorial, cheat sheet, flashcards, quick test, and more.
- A company’s liabilities include every debt it has incurred.
- The balance of the total assets after considering all of the above transactions amounts to $36,450.
For example, if the total liabilities of a business are $50K and the owner’s equity is $30K, then the total assets must equal $80K ($50K + $30K). Valid financial transactions always result in a balanced accounting equation which is the fundamental characteristic of double entry accounting (i.e., every debit has a corresponding credit). Revenues and expenses directly impact equity through retained earnings. Revenues are the inflows of resources from the company’s primary activities, while expenses are the outflows incurred to generate those revenues. The difference between revenues and expenses results in net income or loss.
Your Financial Accounting tutor
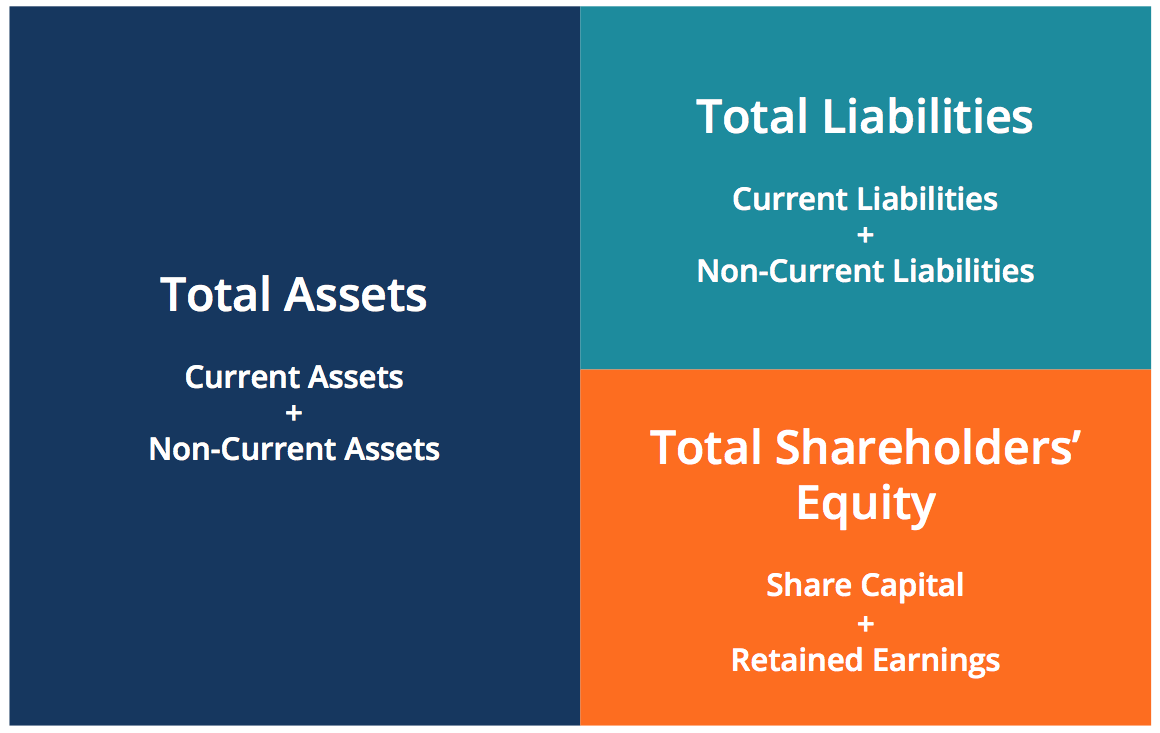

Accounting equation describes that the total value of assets of a business entity is always equal to its liabilities plus owner’s equity. This equation is the foundation of modern double entry system of accounting being used by small proprietors to large multinational corporations. Other names used for this equation are balance sheet equation and fundamental or basic accounting equation. As you can see, no matter what the transaction is, the accounting equation will always balance because each transaction has a dual aspect. The owner’s equity is the balancing amount in the accounting equation. So whatever the worth of assets and liabilities of a business are, the owners’ equity will always be the remaining amount (total assets MINUS total liabilities) that keeps the accounting equation in balance.
A. Basic Accounting Principles
So liability, well this is money that the company owes to other people, right? What’s when we have to pay them in under 1 year, right? Just like with our current assets and long term assets, we have the same threshold of 1 year.
That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions. Consider a company with assets totaling $100,000, liabilities of $60,000, and equity of $40,000. This scenario illustrates the accounting equation perfectly, demonstrating how the components interact. The three primary components of the accounting equation are assets, liabilities, and equity.
Whatever happens, the transaction will always result in the accounting equation balancing. After six months, Speakers, Inc. is growing rapidly and needs to find a new place of business. Ted decides it makes the most financial sense for Speakers, Inc. to buy a building. Since Speakers, Inc. doesn’t have $500,000 in cash to pay for a building, it must take out a loan. Speakers, Inc. purchases a $500,000 building by paying $100,000 in cash and taking out a $400,000 mortgage.
In our examples below, we show how a given transaction affects the accounting equation. We also show how the same transaction affects specific accounts by providing the journal entry that is used to record the transaction in the company’s general ledger. While the accounting equation is essential, it has limitations. It does not account for intangible assets or the complexities of modern financial transactions.
Assets represent everything a company owns, liabilities are its obligations, and equity is the residual interest of the owners. Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations. Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity represent how the assets of a company are financed.
In this form, it is easier to highlight the relationship between shareholder’s equity and debt (liabilities). As you can see, shareholder’s equity is the remainder after liabilities have been subtracted from assets. This is because creditors – parties that lend money such as banks – have the first claim to a company’s assets.
The assets of the business will increase by $12,000 as a result of acquiring the van (asset) but will also decrease by an equal amount due to the payment of cash (asset). Capital essentially represents how much the owners have invested into the business along with any accumulated retained profits or losses. The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner. Ted is an entrepreneur who wants to start a company selling speakers for car stereo systems.


















