Analyze in Material Price and Efficiency Variances in Cost Accounting

As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider retraining workers to reduce waste or change their production process to decrease materials needs per box. Let’s assume that you decide to hire an unskilled worker for $9 per hour instead of a skilled worker for the standard cost of $15 per hour. In this case, the actual quantity of materials used is \(0.50\) pounds, the standard price per unit of materials is \(\$7.00\), and the standard quantity used is \(0.25\) pounds. To illustrate standard costs variance analysis for variable manufacturing overhead, refer to the data for NoTuggins in Exhibit 8-1 above. Per the standards, the variable manufacturing overhead rate is $3 and each unit requires 0.25 direct labor hours.
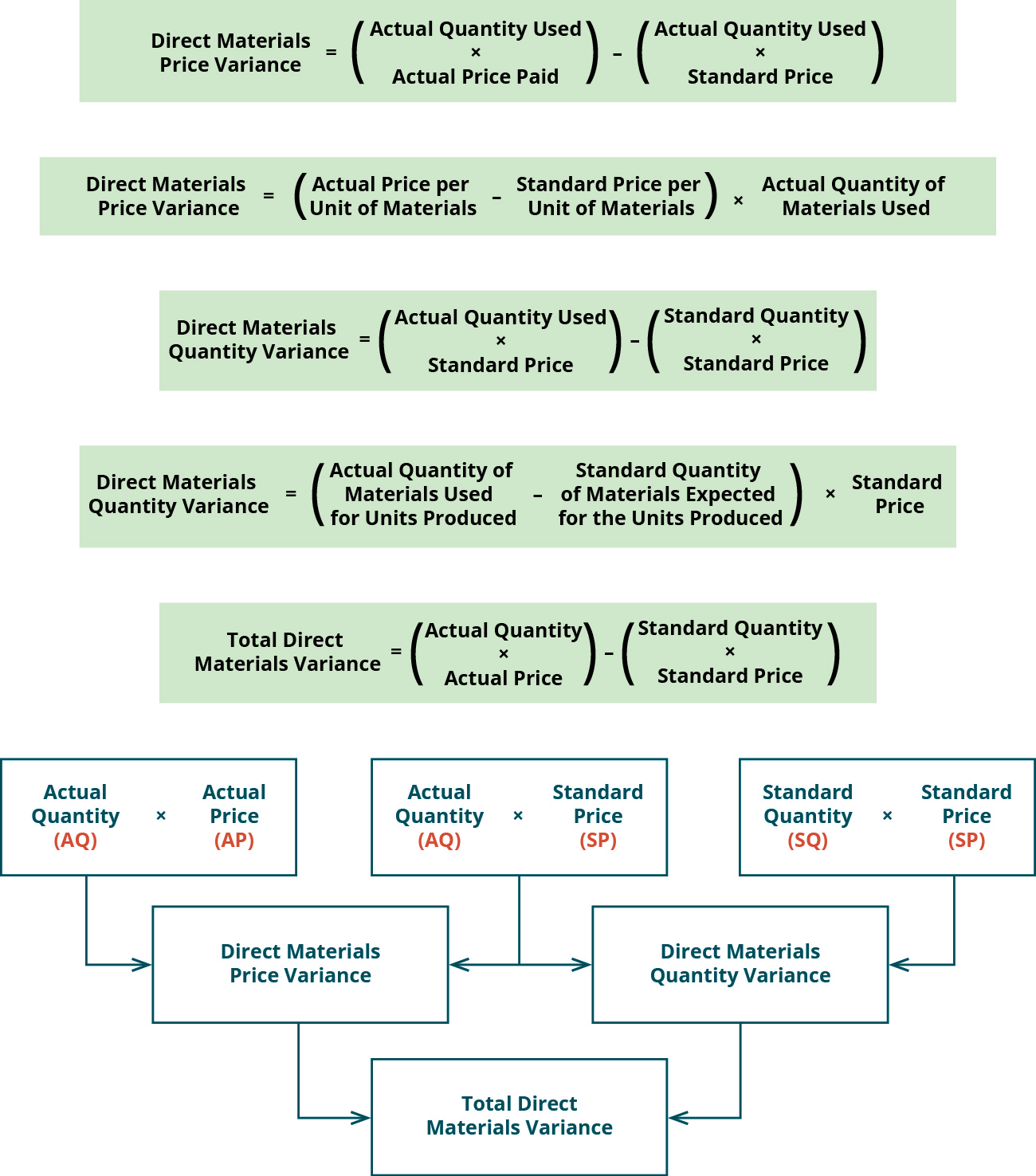
Total Direct Materials Cost Variance
The organization spent $135,000 for the direct labor hours that exceeded the standard number of hours allowed. An investigation may reveal that employees took longer than 0.25 hours to make each unit, which could mean additional training or another appropriate solution. Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct materials variance template, compute the direct materials turbotax deluxe 2011 federal and state returns, pc windows variances. Another key component of any efficiency variance is the basis upon which the standard is set. For example, the number of units of direct material could assume the absence of scrap, when in fact a standard amount of scrap is normally realized, causing a continuing negative efficiency variance. This would be a theoretical standard, that can only be met if the circumstances are optimal.
Material Variances FAQs
- If more than \(600\) tablespoons of butter were used, management would investigate to determine why.
- The variable manufacturing overhead efficiency and rate variances are used to determine if the overall variance is an efficiency issue, rate issue, or both.
- Therefore, companies must monitor and manage efficiency variance to optimize operations and remain competitive.
- Inadequate quality control can result in defective products, rework, and increased costs.
- (Alternative account titles include Direct Materials Quantity Variance or Direct Materials Efficiency Variance.) We will demonstrate this variance with the following information.
If the direct labor is not efficient when producing the good output, there will be an unfavorable labor efficiency variance. That inefficiency will likely cause additional variable manufacturing overhead which will result in an unfavorable variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance. If the inefficiencies are significant, the company might not be able to produce enough good output to absorb the planned fixed manufacturing overhead costs. This in turn can also cause an unfavorable fixed manufacturing overhead volume variance.
What is the difference between labor yield and mix variances?
The total direct materials variance is calculated as the total standard costs allowed for direct materials of $315,000 less the actual amount paid of $330,000 equal the total direct materials variance of $(15,000) U. The efficiency variance is the difference between the actual unit usage of something and the expected amount of it. The expected amount is usually the standard quantity of direct materials, direct labor, machine usage time, and so forth that is assigned to a product. For example, an efficiency variance can be calculated for the number of hours required to complete an audit versus the budgeted amount. Throughout our explanation of standard costing we showed you how to calculate the variances. In the case of direct materials and direct labor, the variances were recorded in specific general ledger accounts.
Direct materials quantity variance
The combination of the two variances can produce one overall total direct materials cost variance. Another strategy involves optimizing production processes through lean manufacturing principles. Techniques such as value stream mapping can help identify and eliminate waste, thereby improving efficiency. For instance, by analyzing the flow of materials and information through the production process, companies can pinpoint bottlenecks and implement changes to streamline operations.
This lesser quality denim causes the production to be a bit slower as workers spend additional time working around flaws in the material. In addition to this decline in productivity, you also find that some of the denim is of such poor quality that it has to be discarded. Further, some of the finished aprons don’t pass the final inspection due to occasional defects not detected as the aprons were made.
Employees may resist changes in their work processes, especially if it involves new technology or new ways of doing things. A comprehensive training program that covers all aspects of the manufacturing operation should be developed, including equipment operation, quality control, safety, and efficiency. The program should include both classroom and hands-on training to ensure that employees understand the concepts and can apply them in the workplace. Efficiency variance can have a significant impact on the company’s profitability.


Even though the answer is a positive number, the variance is unfavorable because more materials were used than the standard quantity allowed to complete the job. If the standard quantity allowed had exceeded the quantity actually used, the materials usage variance would have been favorable. That component of a product that has not yet been placed into the product or into work-in-process inventory. A manufacturer must disclose in its financial statements the actual cost of materials on hand as well as its actual cost of work-in-process and finished goods. That part of a manufacturer’s inventory that is in the production process and has not yet been completed and transferred to the finished goods inventory. This account contains the cost of the direct material, direct labor, and factory overhead placed into the products on the factory floor.
The amount of materials used and the price paid for those materials may differ from the standard costs determined at the beginning of a period. A company can compute these materials variances and, from these calculations, can interpret the results and decide how to address these differences. Knowing that variable manufacturing costs were $181,500 over budget is helpful, but it doesn’t isolate the production issue or issues. Therefore, the next step is to individually analyze each component of variable manufacturing costs. The total variable manufacturing costs variance is separated into direct materials variances, direct labor variances, and variable manufacturing overhead variances. Actual manufacturing data are collected after the period under consideration is finished.
Understanding these variances helps in pinpointing inefficiencies that could be costing the business time and money. This insight is essential for making informed decisions about resource allocation and operational improvements. External factors, such as changes in the market or regulations, can affect a company’s ability to address efficiency variance. If employees and management do not see the importance of addressing efficiency variance, it can be challenging to implement practical solutions. Companies focused on short-term results may overlook the long-term benefits of addressing efficiency variance. This can lead to insufficient investment in the necessary resources to address the issue effectively.
Overhead efficiency variance examines the difference between the standard overhead costs allocated for a certain level of production and the actual overhead costs incurred. This variance is important for understanding how well a company is managing its indirect costs, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. For example, if the standard overhead cost for a production run is $10,000 but the actual cost is $12,000, the overhead efficiency variance would be $2,000. Factors that can affect overhead efficiency variance include changes in production volume, equipment efficiency, and administrative processes.












